上一篇帖子讲述了使用MAX78000开发板驱动2.4寸SPI液晶屏,这次使用MAX78000开发板来读取SD卡。对,最终目的,我是想用MAX78000做成一个电子相册。
FAT
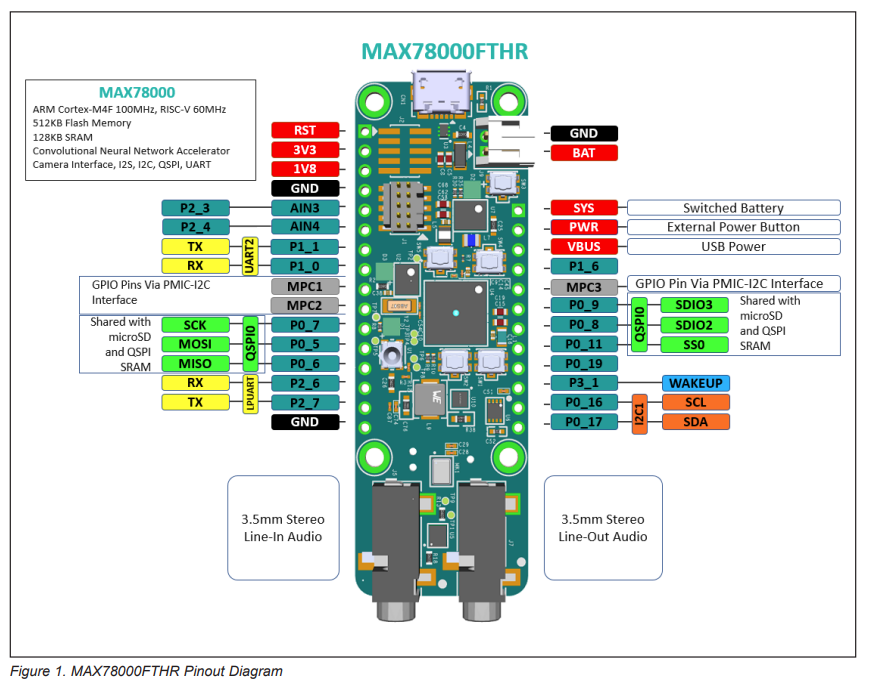
MAX78000FTHR开发板背面有集成一个microSD卡卡槽。通过QSPI0与主控连接。官方例程中“MaximSDK\Examples\MAX78000\SDHC_FTHR”有给出如何使用SD卡的例子。从这个例子中抽取出SD卡操作的函数。
首先创建SD卡的头文件:sd.h,这里创建了4个方法给用户使用。
#include <stdint.h> uint8_t checkCardInserted(void); int read_data(char filename[], uint8_t *type1, uint8_t *type2, float *height, float *weight); int read_bmp(char filename[], uint8_t rgb_image[]); int ls(char cwd[]);
然后是这些方法的具体实现:sd.c
/***** Includes *****/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "board.h"
#include "mxc_delay.h"
#include "mxc_device.h"
#include "gpio.h"
#include "uart.h"
#include "ff.h"
#include "sd.h"
UINT mounted = 0;
TCHAR *FF_ERRORS[20] = {
"FR_OK",
"FR_DISK_ERR",
"FR_INT_ERR",
"FR_NOT_READY",
"FR_NO_FILE",
"FR_NO_PATH",
"FR_INVLAID_NAME",
"FR_DENIED",
"FR_EXIST",
"FR_INVALID_OBJECT",
"FR_WRITE_PROTECTED",
"FR_INVALID_DRIVE",
"FR_NOT_ENABLED",
"FR_NO_FILESYSTEM",
"FR_MKFS_ABORTED",
"FR_TIMEOUT",
"FR_LOCKED",
"FR_NOT_ENOUGH_CORE",
"FR_TOO_MANY_OPEN_FILES",
"FR_INVALID_PARAMETER"
};
FRESULT err; //FFat Result (Struct)
TCHAR cwd[256];
FATFS *fs; //FFat Filesystem Object
FATFS fs_obj;
uint8_t checkCardInserted(void)
{
// On the MAX78000FTHR board, P0.12 will be pulled low when a card is inserted.
mxc_gpio_cfg_t cardDetect;
cardDetect.port = MXC_GPIO0;
cardDetect.mask = MXC_GPIO_PIN_12;
cardDetect.func = MXC_GPIO_FUNC_IN;
cardDetect.pad = MXC_GPIO_PAD_NONE;
cardDetect.vssel = MXC_GPIO_VSSEL_VDDIOH;
MXC_GPIO_Config(&cardDetect);
// Exit function if card is already inserted
if (MXC_GPIO_InGet(MXC_GPIO0, MXC_GPIO_PIN_12) == 0) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int mount()
{
fs = &fs_obj;
if ((err = f_mount(fs, "", 1)) != FR_OK) { //Mount the default drive to fs now
printf("Error opening SD card: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
} else {
printf("SD card mounted.\n");
mounted = 1;
}
f_getcwd(cwd, sizeof(cwd)); //Set the Current working directory
return err;
}
int umount()
{
if ((err = f_mount(NULL, "", 0)) != FR_OK) { //Unmount the default drive from its mount point
printf("Error unmounting volume: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
} else {
printf("SD card unmounted.\n");
mounted = 0;
}
return err;
}
int read_data(char filename[], uint8_t *type1, uint8_t *type2, float *height, float *weight)
{
FIL file; //FFat File Object
UINT bytes_read;
if (!mounted)
mount();
if ((err = f_open(&file, filename, FA_READ)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error opening file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
// Type1 is encoded in uint8
if ((err = f_read(&file, type1, 1, &bytes_read)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error reading file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
// Type2 is encoded in uint8
if ((err = f_read(&file, type2, 1, &bytes_read)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error reading file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
// Height is encoded in float
if ((err = f_read(&file, height, 4, &bytes_read)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error reading file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
// Weight is encoded in float
if ((err = f_read(&file, weight, 4, &bytes_read)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error reading file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
if ((err = f_close(&file)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error closing file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
return 0;
}
int read_bmp(char filename[], uint8_t rgb_image[])
{
FIL file; //FFat File Object
UINT bytes_read;
uint8_t *ptr = rgb_image;
// int height = 60, width = 60;
if (!mounted)
mount();
if ((err = f_open(&file, filename, FA_READ)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error opening file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
// Image data begins at 0x54
if ((err = f_lseek(&file, 54)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error seeking file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
do
{
if ((err = f_read(&file, ptr, 255, &bytes_read)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error reading file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
ptr += 255;
} while (bytes_read == 255); // bytes_read<255 means the cursor reached EOF
if ((err = f_close(&file)) != FR_OK) {
printf("Error closing file: %s\n", FF_ERRORS[err]);
f_mount(NULL, "", 0);
return err;
}
return 0;
}
int ls(char cwd[])
{
DIR dir;
FILINFO fno;
if (!mounted) {
mount();
}
printf("Listing Contents of %s - \n", cwd);
if ((err = f_opendir(&dir, cwd)) == FR_OK) {
while (1) {
err = f_readdir(&dir, &fno);
if (err != FR_OK || fno.fname[0] == 0) {
break;
}
printf("%s", fno.fname);
if (fno.fattrib & AM_DIR) {
printf("/");
}
printf("\n");
}
f_closedir(&dir);
} else {
printf("Error opening directory!\n");
return err;
}
printf("\nFinished listing contents\n");
return err;
}准备好一张microSD卡,然后用FAT文件系统格式化,存放一些文件到卡里。


依然使用上一个帖子的工程,将sd.h和sd.c文件拷贝到项目文件夹内。在main.c文件开头处引入sd.h文件。
#include "sd.h"
然后修改main()函数,这里仅仅是读取SD卡,显示SD卡的文件列表。
int main(void) {
int count = 0;
MXC_Delay(200000);
MXC_ICC_Enable(MXC_ICC0);
/* Set system clock to 100 MHz */
MXC_SYS_Clock_Select(MXC_SYS_CLOCK_IPO);
SystemCoreClockUpdate();
while (1) {
ls("/");
LED_On(LED1);
MXC_Delay(500000);
LED_Off(LED1);
MXC_Delay(500000);
printf("count : %d\n", count++);
}
}使用串口工具打开串口,可以看见板子重复读取SD卡文件列表,并通过串口打印。

 23
23